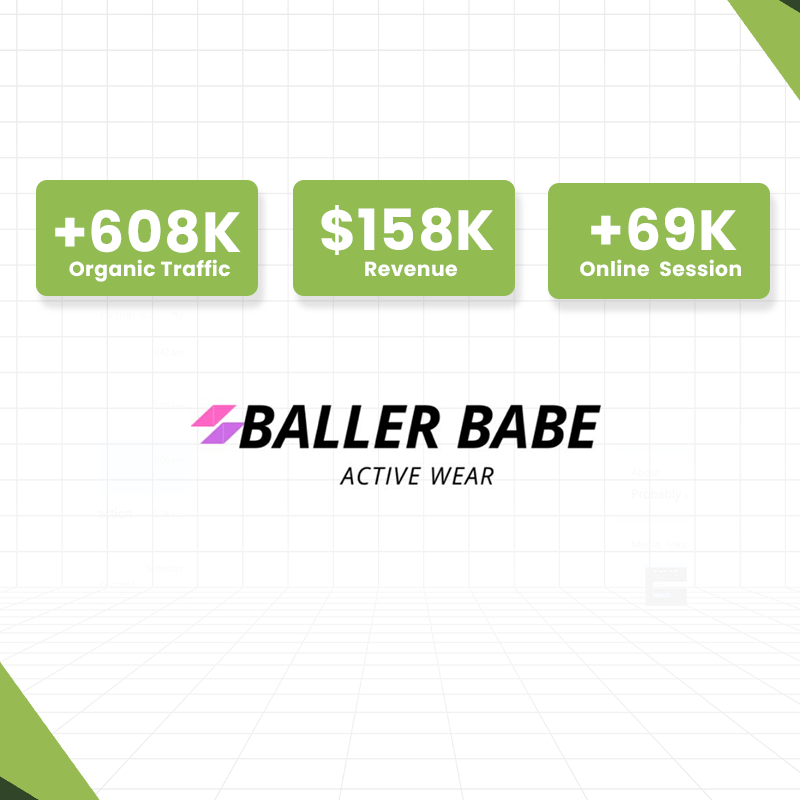
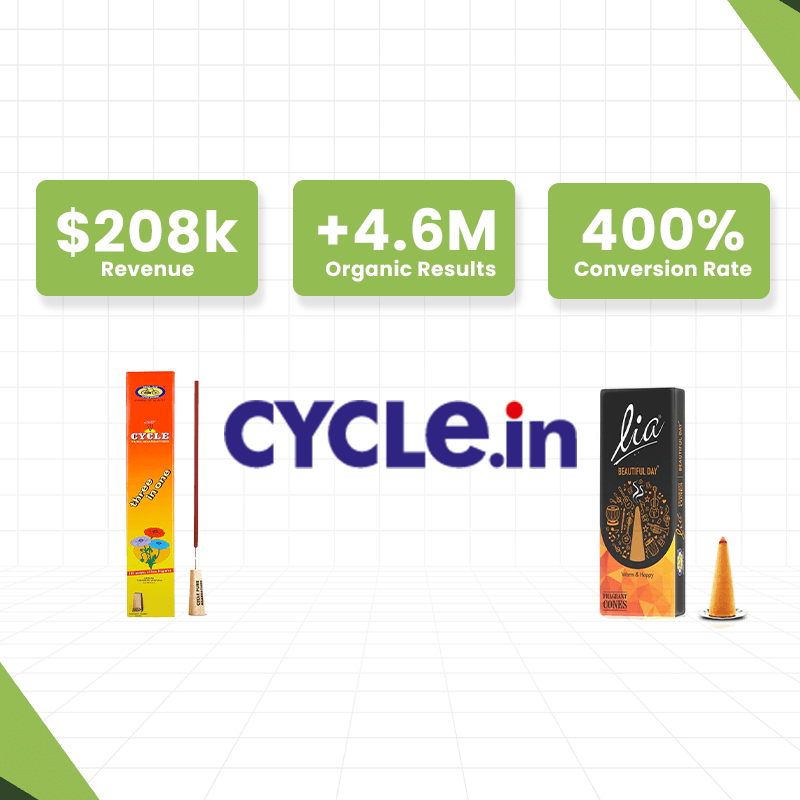
Are you thinking of launching an online store? One of the most crucial decisions you'll face is choosing the right order fulfillment method. With the rise of digital commerce, understanding the differences between dropshipping and traditional ecommerce fulfillment can set your business on the path to success.
Understanding Order Fulfillment
Before diving into dropshipping and ecommerce, let’s outline the traditional ecommerce workflow:
- Customer Visits: A customer browses your online store and selects a product.
- Checkout: The customer completes their purchase.
- Product Handling: The product is picked from your warehouse.
- Packing and Shipping: The order is packed and shipped to the customer.
This process is crucial for efficient order fulfillment, and both ecommerce and dropshipping models utilize it, albeit differently.
How Dropshipping Works
Dropshipping is a specific ecommerce model where the retailer does not hold inventory. Instead, you partner with a dropshipping supplier who fulfills the orders for you. Here’s how it operates:
- You list products on your store without owning the inventory.
- A customer places an order and pays online.
- You forward the order to your dropshipper.
- The dropshipper picks, packs, and ships the product directly to your customer.
This model allows you to start a business without upfront inventory costs, making it an attractive option for many entrepreneurs.
Similarities Between Ecommerce and Dropshipping
Both models share common ground in several areas:
- Building a website
- Uploading product catalogs
- Designing the checkout flow
- Marketing and advertising products
Key Differences: Dropshipping vs. Ecommerce
While both methods follow similar workflows, they differ significantly in several aspects:
1. Initial Investment
- Dropshipping: Minimal initial investment since there’s no need for inventory.
- Ecommerce: Requires capital to purchase inventory and set up warehousing.
2. Profitability
- Dropshipping: Generally lower profit margins due to the middleman (the dropshipper).
- Ecommerce: Higher profit margins by purchasing products at wholesale prices.
3. Ease of Business
- Dropshipping: Easier for beginners; no upfront product costs or storage worries.
- Ecommerce: More complex as you need to manage inventory and logistics.
4. Branding Control
- Dropshipping: Limited control over product quality and branding.
- Ecommerce: Full control over the product selection and branding, enabling you to create a strong brand identity.
5. Risk Management
- Dropshipping: Low risk of unsold inventory; however, legal risks may arise from third-party vendors.
- Ecommerce: Higher risk of loss if products don’t sell, but you maintain control over operations.
When to Choose Dropshipping
Opt for dropshipping if:
- You’re a beginner looking to launch quickly.
- You want to minimize startup costs.
- You’re selling non-branded products.
- You want to mitigate the risks of unsold inventory.
When to Choose Ecommerce Fulfillment
Consider ecommerce fulfillment if:
- You have sufficient funds and a capable team.
- You’re selling your own branded products.
- You want full control over your fulfillment processes.
Final Thoughts: Making Your Decision
Both dropshipping and ecommerce have their advantages and challenges. Your choice will depend on factors such as your initial investment capability, desired profit margins, and level of control over branding.
Whichever model you choose, focus on creating a seamless online shopping experience to build a loyal customer base. Are you ready to embark on your ecommerce journey? Understanding these fulfillment methods is your first step toward success!